17 KiB
屏幕后期处理效果
在渲染完整个场景之后,得到的屏幕图像进行了一系列操作,最终实现各种屏幕特效,如Bloom,SSAO等等。
要实现屏幕后期处理的基础是,必须得到渲染后的屏幕图像,即抓取屏幕,而Unity为我们提供了这样一个方便的接口---OnRenderImage函数。
写在前面
简单介绍几个常用名词。
0.1 UV
U和V分别是图片在显示器水平、垂直方向上的坐标,取值范围是0~1。通常是从左往右,从下往上从0开始依次递增。
1.基础类
在进行屏幕后期处理之前,我们需要检查一系列条件是否满足,例如当前平台是否支持渲染纹理跟屏幕特效。是否支持当前使用的shader等。为此,我们创建了一个用于屏幕后期处理效果的基类。在实现各种屏幕特效时,我们只需继承基础类。在实现派生类中不同操作即可。
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
[ExecuteInEditMode]
[RequireComponent (typeof(Camera))]
public class PostEffectsBase : MonoBehaviour {
// 开始检查
protected void CheckResources() {
bool isSupported = CheckSupport();
if (isSupported == false) {
NotSupported();
}
}
// 在检查是否支持屏幕后期shader的时候调用
protected bool CheckSupport() {
if (SystemInfo.supportsImageEffects == false || SystemInfo.supportsRenderTextures == false) {
Debug.LogWarning("This platform does not support image effects or render textures.");
return false;
}
return true;
}
// 在不支持屏幕后期shader的时候调用。
protected void NotSupported() {
enabled = false;
}
protected void Start() {
CheckResources();
}
// 在需要通过该屏幕后期shader创建相应材质的时候调用。
protected Material CheckShaderAndCreateMaterial(Shader shader, Material material) {
if (shader == null) {
return null;
}
if (shader.isSupported && material && material.shader == shader)
return material;
if (!shader.isSupported) {
return null;
}
else {
material = new Material(shader);
material.hideFlags = HideFlags.DontSave;
if (material)
return material;
else
return null;
}
}
}
基础类使用案例(继承PostEffectBase)
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class ImageEffectGeneral : PostEffectsBase{
public Shader scannerShader;
private Material scannerMaterial;
public Material material
{
get
{
// 检查是否生成对应材质
scannerMaterial = CheckShaderAndCreateMaterial(scannerShader, scannerMaterial);
return scannerMaterial;
}
}
//定义相关数据调整
public string dataTags = "";
public float dataScale = 1.0f;
public new void Start()
{
//如果需要提前规定Camera获取深度纹理或者法线纹理,需要提前声明
//GetComponent<Camera>().depthTextureMode = DepthTextureMode.DepthNormals;
}
void OnRenderImage(RenderTexture src, RenderTexture dest)
{
//GetComponent<Camera>().depthTextureMode = DepthTextureMode.DepthNormals;
if (material != null)
{
//需要传入的数据,需要在Shader中定义好对应变量名称,作为传入依据。
material.SetFloat(dataTags, dataScale);
Graphics.Blit(src, dest, material);
}
else
{
Graphics.Blit(src, dest);
}
}
}
2.使用渲染纹理
在Unity中,获取深度纹理是非常简单的,直接在脚本中设置摄像机的depthTextureMode,就可以获取对应的纹理数据。
深度纹理获取
GetComponent<Camera>().depthTextureMode = DepthTextureMode.Depth;
法线纹理+深度纹理获取:
GetComponent<Camera>().depthTextureMode = DepthTextureMode.DepthNormals;
深度纹理采样
当在Shader中访问到深度纹理 _CameraDepthTexture 后,我们就可以使用当前像素的纹理坐标对它进行采样。绝大多数情况下,我们直接使用tex2D函数采样即可,但在某些平台(例如PS3或者PSP)上,我们需要一些特殊处理。Unity为我们提供了一个统一的宏,SAMPLE_Depth_Texture,用来处理这些由于平台差异造成的问题。
法线纹理采样
用以下语句进行的法线采样,是范围在-1~1之间的水平&垂直法线值,如果需要展示成法线贴图,需要手动对normal进行归一化处理 normal = 0.5*normal+0.5
fixed3 normal = DecodeViewNormalStereo(tex2D(_CameraDepthNormalsTexture,i.uv));
屏幕后期处理效果实例
1.uv应用:扭曲
通过重新计算uv,采用黑白图来对uv进行重新赋值,可以产生扭曲的效果。
Shader "Hidden/ImageDistort"
{
Properties
{
_MainTex ("Texture", 2D) = "white" {}
_DistortTex ("Distort Texture", 2D) = "white" {}
_DistortScale ("Distort Scale",Range(0,1)) = 1.0
}
SubShader
{
// No culling or depth
Cull Off ZWrite Off ZTest Always
Pass
{
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
sampler2D _MainTex;
sampler2D _DistortTex;
float _DistortScale;
struct appdata
{
float4 vertex : POSITION;
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
};
struct v2f
{
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
float4 vertex : SV_POSITION;
};
v2f vert (appdata v)
{
v2f o;
o.vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
o.uv = v.uv;
return o;
}
fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target
{
//i.uv = abs(0.5-i.uv);
fixed4 noise = tex2D(_DistortTex,i.uv);
i.uv = i.uv + (0.5-noise.r) * _DistortScale*0.1;
fixed4 col = tex2D(_MainTex, i.uv);
// just invert the colors
//col.rgb = 1 - col.rgb;
return col;
}
ENDCG
}
}
}
使用时,可以参考上述中的,基础类使用案例,编写对应的cs脚本并挂在摄像机上,通过调整相关参数来观看对应效果
2.深度纹理应用:扫描效果探究
深度图的每一个像素值表示场景中某点与摄像机的距离。
是指将从图像采集器到场景中各点的距离(深度)作为像素值的图像,它直接反映了景物可见表面的几何形状。
shader中,深度图的获取可以通过以下代码进行
float depth = SAMPLE_DEPTH_TEXTURE(_CameraDepthTexture,i.uv);
float linearDepth = Linear01Depth(depth);
fixed4 col = fixed4(linearDepth,linearDepth,linearDepth,1);
当通过纹理采样SAMPLE_DEPTH_TEXTURE之后,得到的深度值往往是非线性的。然而,我们的计算过程中通常是需要线性的深度值,也就是说,我们需要把投影后的深度值变换到线性空间下。
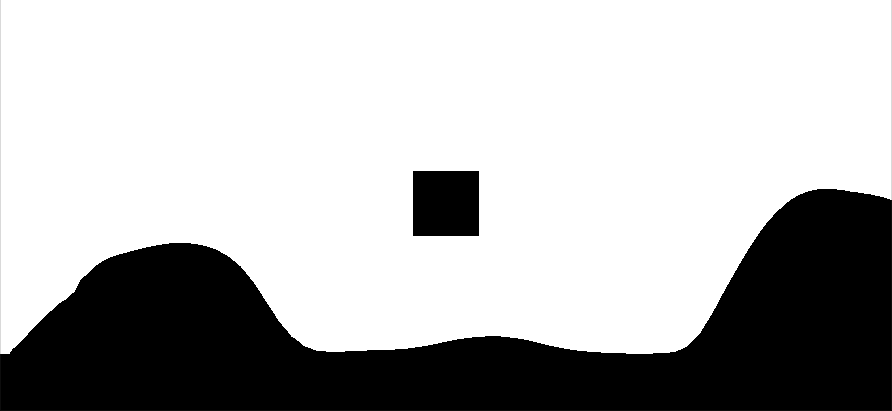
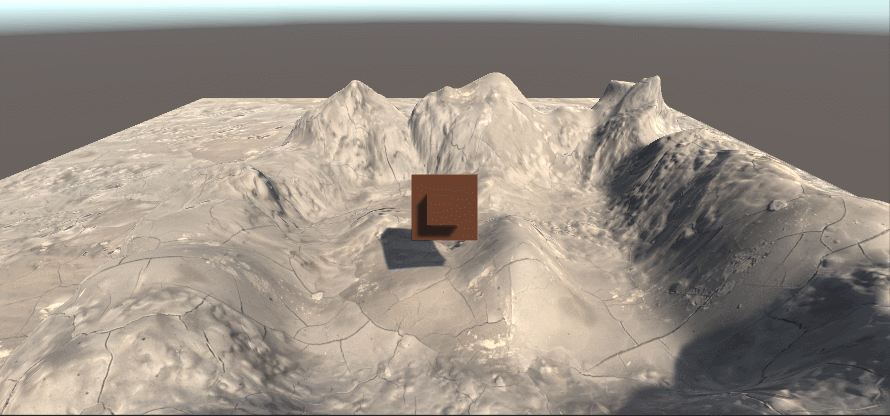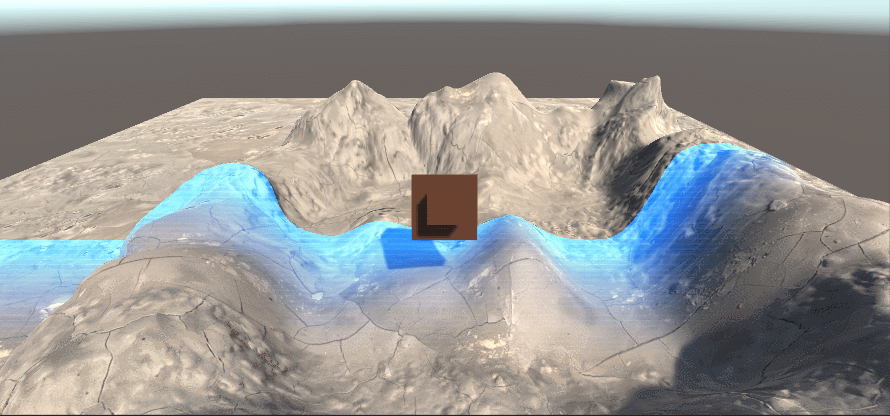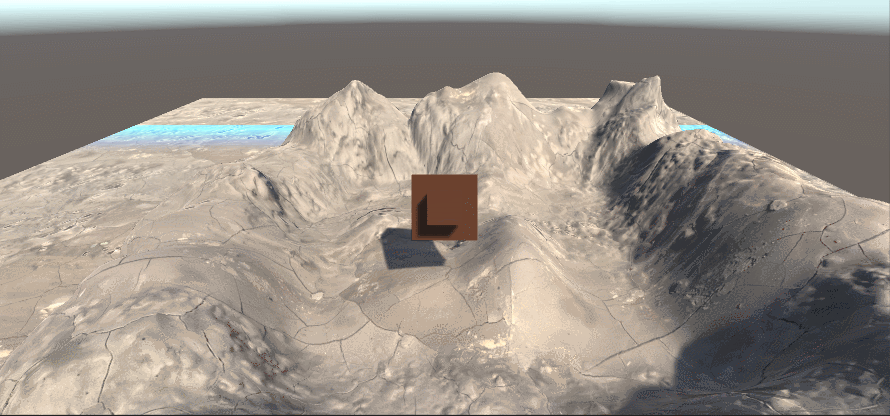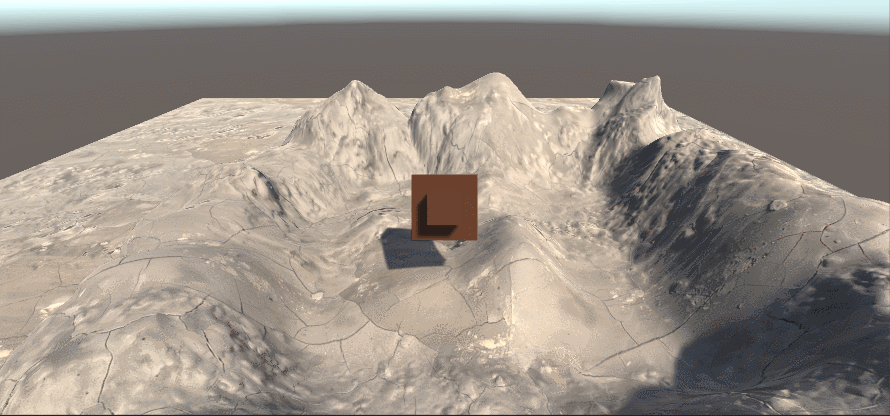
最终结果如下,上图为原始场景,下图为场景中提取的深度图(通过Linear01Depth解码)
0表示该点和摄像机处于同一位置,1表示该点位于视锥体的远裁剪平面上(摄像机Near=0.3 Far=50)
LinearEyeDepth负责把深度纹理的采样结果转换到视角空间下的深度值
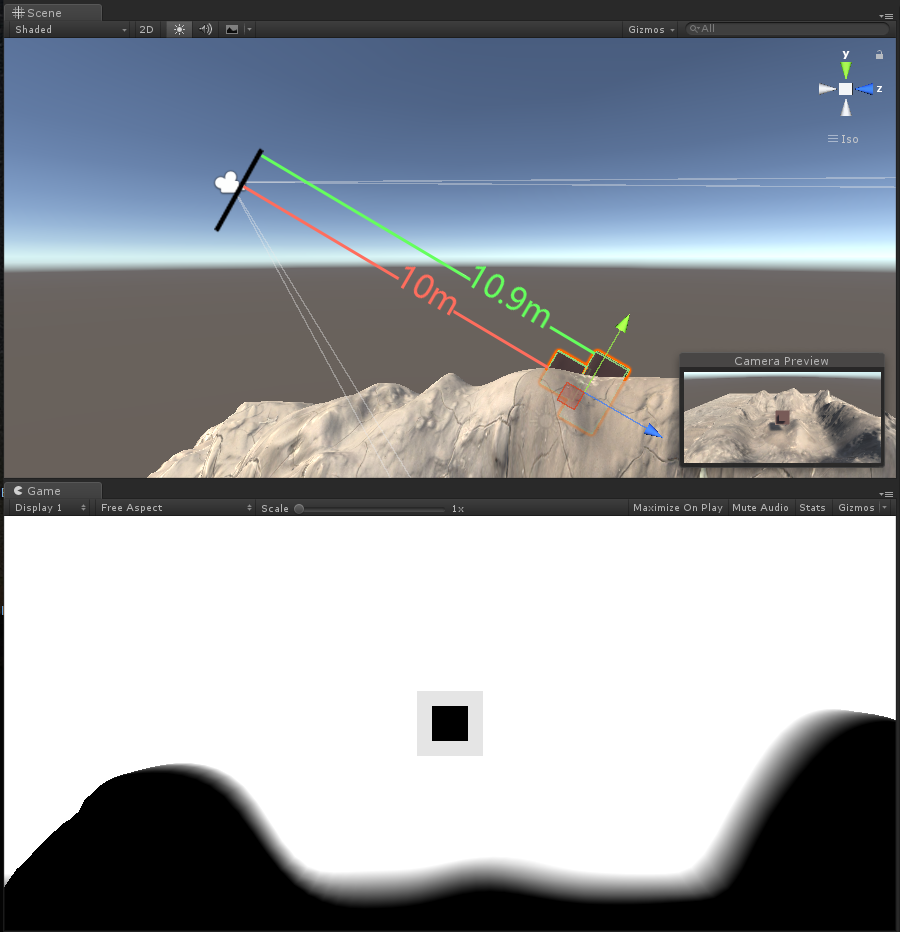
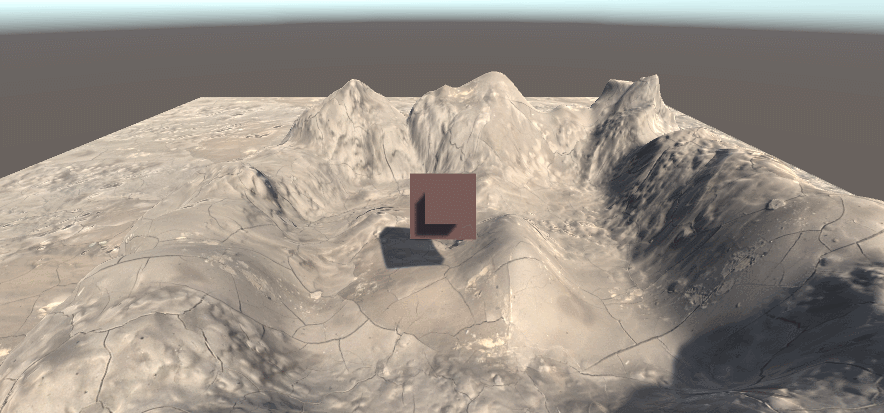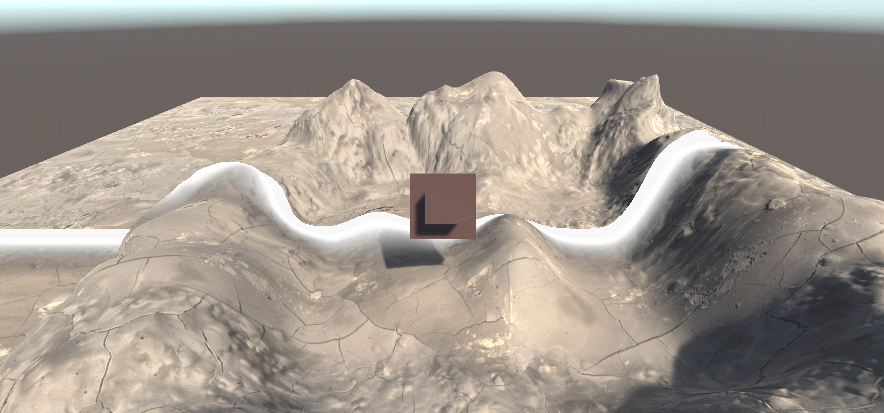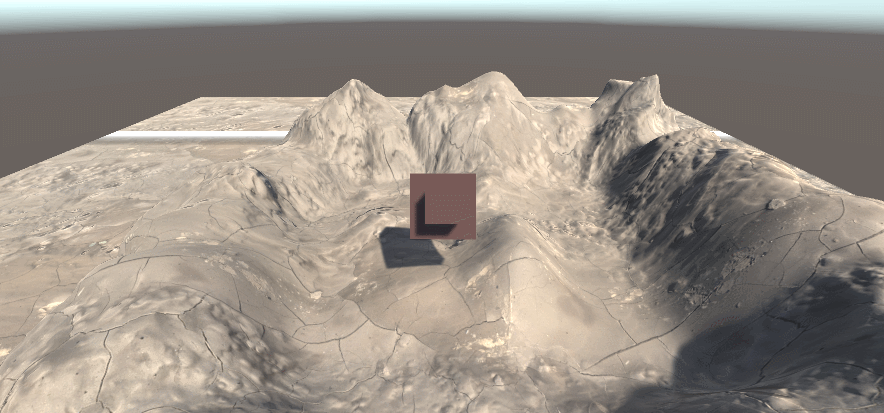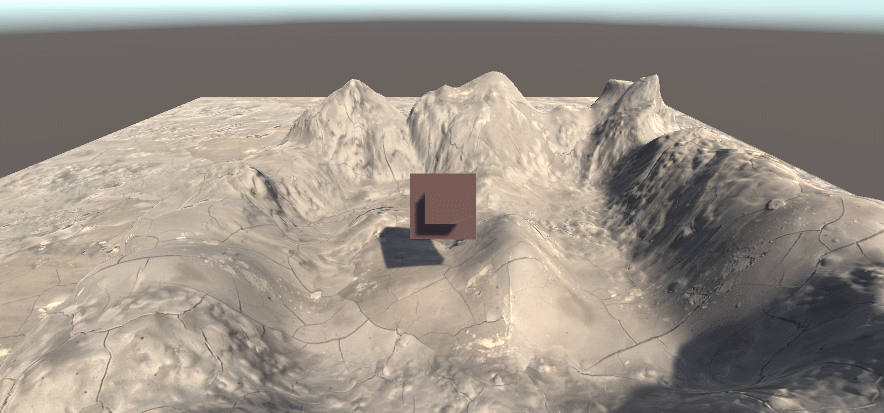
LinearEyeDepth解码,此时的摄像机远裁剪平面与近裁剪平面并不会对结果产生影响,通过调节参数_DepthParam,看对应的变化区间(下图为_DepthParam为10的样子,即黑的部分是离镜头10m以内的,白色部分是离镜头11m以外的,模糊的部分为距离10-11m之间的值)
float depth = SAMPLE_DEPTH_TEXTURE(_CameraDepthTexture,i.uv);
float linearDepth = LinearEyeDepth(depth);
float diff = linearDepth-_DepthParam;
使用floor函数,对上述的值进行取整,并对采样值归一化,可以得到比较尖锐化的边缘,此时深度在11m范围内的部分会全部变成黑色。
float depth = SAMPLE_DEPTH_TEXTURE(_CameraDepthTexture,i.uv);
float linearDepth = LinearEyeDepth(depth);
float diff = linearDepth-_DepthParam;
diff = saturate(floor(diff));
通过负数取值归一化,可对采样值进行反色,让黑的部分变白,白的部分变黑。
float depth = SAMPLE_DEPTH_TEXTURE(_CameraDepthTexture,i.uv);
float linearDepth = LinearEyeDepth(depth);
float diff = linearDepth-_DepthParam;
diff = saturate(-diff);
上述操作中,如果不进行归一化(取值范围限制在0-1之间)的话,黑的部分可能会产生负数,白的部分可能会超过1,最终可能计算不出正确结果。
将上述两张图按加算合起来,得到一个按深度扫描的效果雏形
float depth = SAMPLE_DEPTH_TEXTURE(_CameraDepthTexture,i.uv);
float linearDepth = LinearEyeDepth(depth);
float diff = linearDepth-_DepthParam;
diff = saturate(floor(diff))+saturate(-diff);
得到这部分后,因为归一化前面已经做过了,我们仅需要对上述结果进行反色处理(1-diff),再混合上原背景(对原图像进行插值处理,此时我们用到前面所提到的插值函数lerp),就可以看到对应的扫描效果了。
fixed4 mainTex = tex2D(_MainTex, i.uv);
float depth = SAMPLE_DEPTH_TEXTURE(_CameraDepthTexture,i.uv);
float linearDepth = LinearEyeDepth(depth.r);
fixed4 col = fixed4(linearDepth,linearDepth,linearDepth,1);
float diff = linearDepth-_DepthParam;
fixed4 border = 1-(saturate(floor(diff))+saturate(-diff*0.5));
fixed4 final = lerp(mainTex,border*_DepthColor,border);
return final;
下面提供完整代码
ExampleScannerImage.shader
Shader "Hidden/ExampleScannerImage"
{
Properties
{
_MainTex ("Texture", 2D) = "white" {}
_DepthParam ("DepthParam",Float) = 1.0
_DepthColor("DepthColor",Color) = (1,1,1,1)
}
SubShader
{
// No culling or depth
Cull Off ZWrite Off ZTest Always
Pass
{
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
sampler2D _MainTex;
sampler2D _CameraDepthTexture;
float _DepthParam;
fixed4 _DepthColor;
struct appdata
{
float4 vertex : POSITION;
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
};
struct v2f
{
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
float4 vertex : SV_POSITION;
};
v2f vert (appdata v)
{
v2f o;
o.vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
o.uv = v.uv;
return o;
}
fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target
{
fixed4 mainTex = tex2D(_MainTex, i.uv);
float depth = SAMPLE_DEPTH_TEXTURE(_CameraDepthTexture,i.uv);
float linearDepth = LinearEyeDepth(depth.r);
float diff = linearDepth-_DepthParam;
fixed4 border = 1-(saturate(floor(diff))+saturate(-diff*0.5));
fixed4 final = lerp(mainTex,border*_DepthColor,border);
return final;
}
ENDCG
}
}
}
PostEffects.cs(参考本篇开头)
ImageScannerEffect.cs
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class ImageScannerEffect : PostEffectsBase
{
public Shader scannerShader;
private Material scannerMaterial;
public Material material
{
get
{
// 检查是否生成对应材质
scannerMaterial = CheckShaderAndCreateMaterial(scannerShader, scannerMaterial);
return scannerMaterial;
}
}
//定义相关数据调整
public float dataScale = 1.0f;
public Color dataColor = Color.white;
void OnRenderImage(RenderTexture src, RenderTexture dest)
{
//GetComponent<Camera>().depthTextureMode = DepthTextureMode.DepthNormals;
if (material != null)
{
material.SetFloat("_DepthParam", dataScale);
material.SetColor("_DepthColor", dataColor);
Graphics.Blit(src, dest, material);
}
else
{
Graphics.Blit(src, dest);
}
}
}
使用时,将ImageScannerEffect.cs拖拽至主摄像机中,并且把ExampleScannerImage.shader 这个文件拖至Scanner Shader选项卡中去。
录制动画,调节脚本中DataScale选项依次增大,完成相关扫描特效的制作。
可以根据自己喜好,调整相关颜色等操作。
添加图片遮罩,根据法线纹理生成网格纹理等等我们后续会接着讲。
3.纹理附加:扫描效果探究(续)
在上图中,我们由于为对插值处理进行相关优化,所以在尾部会出现一些黑色的部分,这些黑色的部分是因为原本的图像是呈现黑色的。
这次我们使用一张附加纹理,使得扫描效果更具科技感一些
这次是我们使用的附加纹理原图
在使用上述图片之前,我们需要了解uv转换函数TRANSFORM_TEX
TRANSFORM_TEX方法比较简单,就是将模型顶点的uv和Tiling、Offset两个变量进行运算,计算出实际显示用的定点uv。
如果对_MaskTex这个纹理进行uv转换,必须声明变量_MaskTex_ST(float4类型)
实际调整的时候,_MaskTex_ST.xy代表Tilling(缩放程度),_MaskTex_ST.zw代表Offset(偏移程度)
我们在声明变量的时候,沿用_MaskTex的同时下方添加一个ST的声明即可
sampler2D _MaskTex;
float4 _MaskTex_ST;
float _MaskTexTillY;
片元着色器
_MaskTex_ST.y = _MaskTexTillY;
i.uv = TRANSFORM_TEX(i.uv, _MaskTex);
fixed4 maskTex = tex2D(_MaskTex,i.uv);
在附加纹理时,可以通过两种方式进行,一种是附加法,一种是累乘法
我们这里使用了带颜色的附加法进行(因为包含了黑色,原本是黑色的部分就不会变化)
同样的,我们在原本的基础上使用了_DepthColor.a 作为底图的影响程度,这样可以淡化尾部的黑色部分。
fixed4 final = lerp(mainTex,saturate(border*_DepthColor+mainTex*_DepthColor.a+maskTex*_DepthColor),saturate(border));
改写完shader后,在cs脚本中添加以下内容即可
public Texture dataTex;
public float tillY;
OnRenderImage函数中
material.SetTexture("_MaskTex", dataTex);
material.SetFloat("_MaskTexTillY", tillY);
shader完整代码
Shader "Hidden/ExampleScannerImage"
{
Properties
{
_MainTex ("Texture", 2D) = "white" {}
_MaskTex("Mask Texture", 2D) = "white" {}
_MaskTexTillY("Till Y",Float) = 1.0
_DepthParam ("DepthParam",Float) = 1.0
_DepthColor("DepthColor",Color) = (1,1,1,1)
_DepthLength ("DepthLength",Float) = 1.0
}
SubShader
{
// No culling or depth
Cull Off ZWrite Off ZTest Always
Pass
{
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
sampler2D _MainTex;
sampler2D _CameraDepthTexture;
sampler2D _MaskTex;
float4 _MaskTex_ST;
float _MaskTexTillY;
float _DepthParam;
fixed4 _DepthColor;
float _DepthLength;
struct appdata
{
float4 vertex : POSITION;
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
};
struct v2f
{
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
float4 vertex : SV_POSITION;
};
v2f vert (appdata v)
{
v2f o;
o.vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
o.uv = v.uv;
return o;
}
fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target
{
fixed4 mainTex = tex2D(_MainTex, i.uv);
float depth = SAMPLE_DEPTH_TEXTURE(_CameraDepthTexture,i.uv);
float linearDepth = LinearEyeDepth(depth.r);
float diff = linearDepth-_DepthParam;
fixed4 border = 1-(saturate(floor(diff))+saturate(-diff*_DepthLength));
_MaskTex_ST.y = _MaskTexTillY;
i.uv = TRANSFORM_TEX(i.uv, _MaskTex);
fixed4 maskTex = tex2D(_MaskTex,i.uv);
fixed4 final = lerp(mainTex,saturate(border*_DepthColor+mainTex*_DepthColor.a+maskTex*_DepthColor),saturate(border));
return final;
}
ENDCG
}
}
}
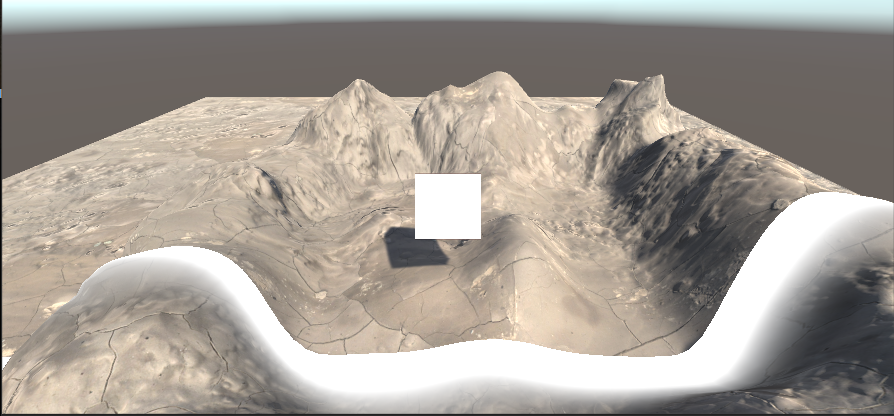
具体效果截图
此时,我们的扫描效果就已经比上一个阶段高出一个档次了